News & Stories
2021

News
HKUST Research Shows Growing Dominance of Diatom Algae in the Pearl River Estuary
It is a common perception that waters close to population would be more polluted than those offshore or at higher latitudes. However, researchers from The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) found that the ratio between two common microalgae diatom and dinoflagellate (dino) – a common benchmark of water quality, has been nearly doubled in the Pearl River Estuary (PRE), one of the world’s most urbanized subtropical coastal waters, over the past two decades.
News
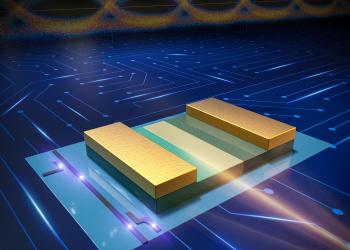
HKUST scientists demonstrated high-performance photodetectors (PDs) grown on SOI for silicon photonics
A research team led by Prof. Kei-May LAU of the Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering at Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has recently developed a novel semiconductor deposition scheme and demonstrated high-performance photodetectors (PDs) grown on silicon-on-insulators (SOI) for silicon photonics. These III-V photodetectors are qualified candidates for high-speed data communications in silicon photonics. These results point to a practical solution for the monolithic integration of III-V active devices and Si-based passive devices on the SOI platform in the future.

News
HKUST Collaborates with HKSAR Government on Solving Regional Ozone Pollution in Greater Bay Area
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) is partnering with the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR) Government in a 3-year groundbreaking cross-border study to monitor the air quality on land, at sea and in the air, which will give us a more in-depth understanding of the formation and transportation of ozone in Hong Kong and across the Greater Bay Area (GBA).

News
HKUST and PolyU researchers develop an in-vitro vesicle formation assay to reveal mechanistic insights into the secretory pathway
Scientists from The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) and The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (PolyU) have developed an in-vitro vesicle formation assay, shedding light on cargo clients and factors that mediate vesicular trafficking and providing a robust tool to offer novel insights into the secretory pathway.

News
HKUST researchers develop technology to extend the horizon of wide-bandgap semiconductor gallium nitride electronics
A research team led by Prof. Kevin Chen of Department of Electronic and Computer Engineering at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has recently inducted a new member, the complementary logic circuitry, into the family of wide-bandgap gallium nitride (GaN) electronics, thereby substantially extending the horizon of the GaN research realm. The functionality and performance of GaN-based electronic devices and integrated circuits are expected to be further improved and become more competitive.

News
HKUST researchers develop a photo-rechargeable lead-free perovskite lithium-ion battery that generates energy and stores battery on a single device
A team of researchers from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has developed an inexpensive, lightweight, and non-toxic (lead-free) photo-battery that has dual functions in harvesting solar energy and storing energy on a single device, making it possible to charge a battery under the sun, without having to plug the device into the wall.










